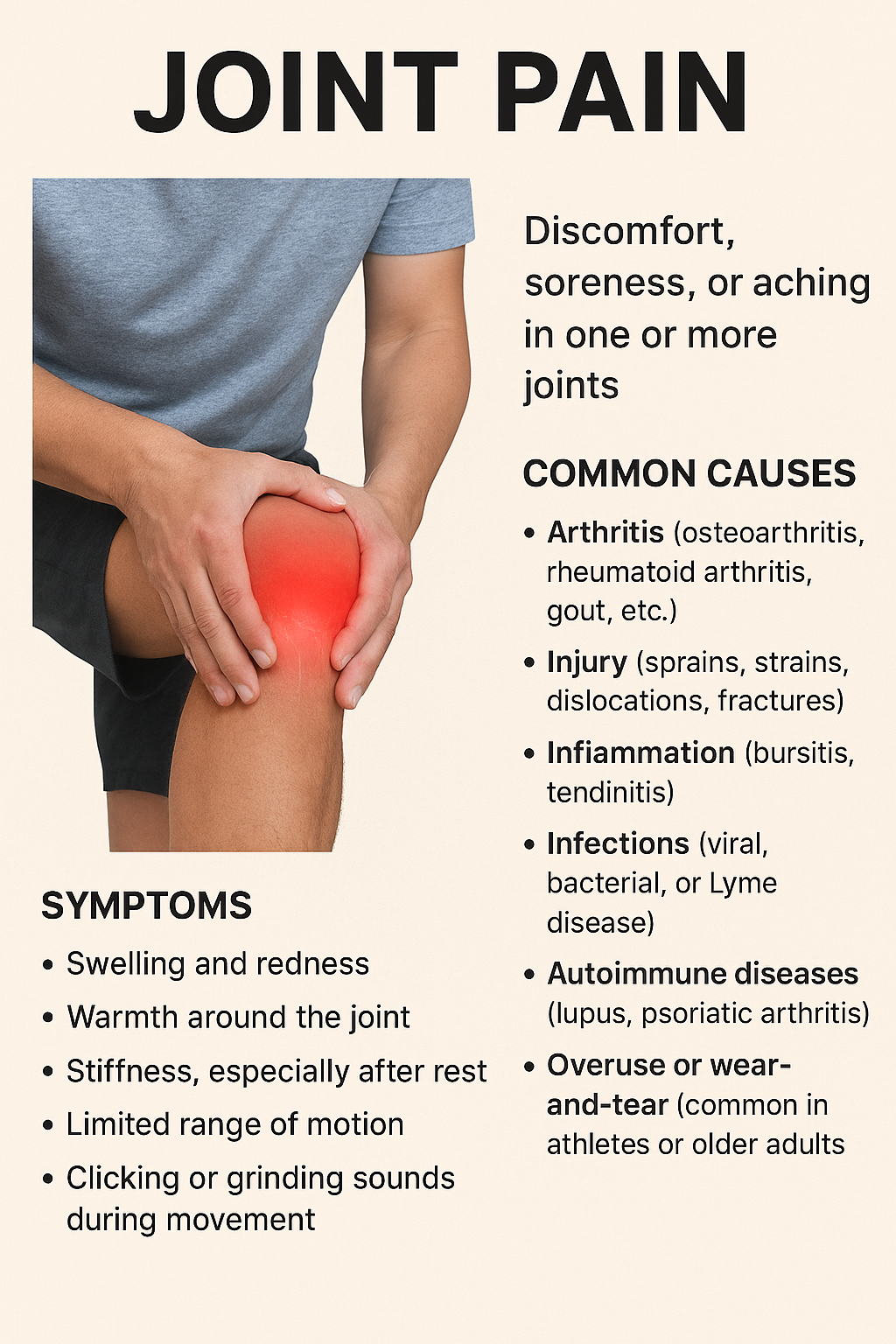
Definition: Discomfort, pain, or inflammation in one or more joints.
Also Known As: Arthralgia.
Impact: May limit movement and interfere with daily activities or quality of life.
Severity: Can range from mild to debilitating; persistent pain should be evaluated by a doctor.
Arthritis:
Osteoarthritis: Degeneration of cartilage.
Rheumatoid arthritis: Autoimmune inflammation of the joints.
Injuries:
Sprains, strains, fractures, or joint dislocations.
Overuse:
Repetitive motion or excessive load on joints.
Other Medical Conditions:
Bursitis: Inflammation of joint cushioning sacs.
Tendinitis: Inflammation of tendons.
Gout: Uric acid crystal buildup.
Infections: Viral or bacterial.
Pain: Sharp, dull, throbbing, or grating sensations.
Stiffness: Especially noticeable in the morning.
Swelling: Joint may feel warm or appear enlarged.
Redness: Around the affected joint.
Limited Range of Motion: Difficulty in joint movement.
Persistent or worsening joint pain.
Swelling, warmth, or redness in the joint.
Pain accompanied by fever, rash, or other systemic symptoms.
Pain interfering with daily activities.
Over-the-Counter Pain Relievers: Ibuprofen, naproxen, acetaminophen.
Ice & Heat Therapy:
Ice: Reduces inflammation.
Heat: Eases stiffness and improves circulation.
Exercise:
Low-impact activities (e.g., swimming, walking).
Physical Therapy:
Enhances strength, flexibility, and joint function.
Prescription Medications:
For severe inflammation or autoimmune causes.
Supplements:
Glucosamine, Chondroitin – may support joint health.
Surgery:
Considered in advanced joint damage (e.g., joint replacement).
Maintain a healthy weight to reduce joint strain.
Engage in regular low-impact exercise.
Warm up before and cool down after physical activity.
Use protective gear during sports or high-risk activities.
Consider nutritional supplements if at risk of joint degeneration.